In the world of wireless communication, WiFi module chips serve as the backbone for connectivity. One crucial aspect to consider is the signal coverage range of these chips. Several factors influence the signal coverage, such as transmission power, frequency, antenna design, environmental conditions, and obstacles.
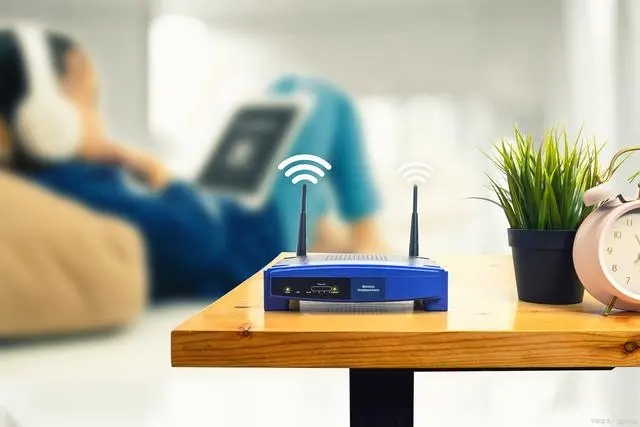

Transmission power determines the strength of the WiFi signal emitted by the module chip. The higher the transmission power, the greater the signal coverage range. It is important to note that the transmission power may be limited by regulatory standards to prevent interference with other devices or networks.
The frequency at which a WiFi module chip operates can impact its signal coverage range. Generally, WiFi chips use the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency bands. The 2.4 GHz band offers better coverage over larger distances, whereas the 5 GHz band provides higher data transfer rates but with shorter coverage range.
The design and quality of the antenna significantly affect the signal coverage range. Antennas can be either internal or external. External antennas generally provide better range as they can be positioned for optimal signal propagation. Antenna gain, which measures the ability to focus the signal in a specific direction, is another factor to consider to enhance coverage.
Environmental factors like walls, doors, furniture, and other obstructions can impact the signal coverage range. Dense materials such as concrete and metal tend to weaken and block WiFi signals. On the other hand, open spaces allow signals to propagate further with minimal obstruction.
Obstacles present within the coverage area, such as walls, floors, and objects, can weaken the WiFi signal. The construction materials and thickness of these barriers determine the extent to which they affect signal coverage. Understanding the layout of the area is essential for optimizing signal strength and range.
To extend the signal coverage range, various signal amplification techniques can be implemented. These include range extenders, repeaters, mesh networks, and signal boosters. By strategically placing these devices, WiFi coverage can be expanded and strengthened throughout a larger area.In conclusion, the signal coverage range of WiFi module chips is influenced by transmission power, frequency, antenna design, environmental conditions, obstacles, and signal amplification techniques. Designing and optimizing these factors help ensure optimal WiFi coverage for a given area, allowing seamless connectivity and enhanced user experience.
 Trolink Joint With Tuya to Make Iot Benefit Every Family
Trolink Joint With Tuya to Make Iot Benefit Every Family
 5 Key Indicators for WiFi Module Selection You Have to Know !
5 Key Indicators for WiFi Module Selection You Have to Know !
 IOT module is the brain of smart products
IOT module is the brain of smart products
 What is the signal coverage range of the WiFi module chip?
What is the signal coverage range of the WiFi module chip?