MQTT and Modbus are two widely used protocols in the Internet of Things (IoT) landscape. While they serve different purposes, they often complement each other, enabling seamless communication and efficient data exchange in IoT systems. This article dives into the details of how MQTT and Modbus work together to enhance the IoT experience.
MQTT, which stands for Message Queuing Telemetry Transport, is a lightweight pub/sub protocol designed for efficient communication in IoT. It uses a publish/subscribe messaging model that enables devices and applications to exchange data in a fast and reliable manner. On the other hand, Modbus is a serial communication protocol that allows communication between devices connected in a master-slave architecture, typically used in industrial applications.
MQTT plays a crucial role in IoT by facilitating easy and efficient data exchange between devices. Its lightweight nature and low bandwidth usage make it ideal for resource-constrained IoT devices. MQTT's publish/subscribe model ensures that data is delivered only to interested subscribers, reducing network load and conserving battery life. With its support for Quality of Service (QoS) levels, MQTT ensures reliable message delivery even in unreliable network conditions.
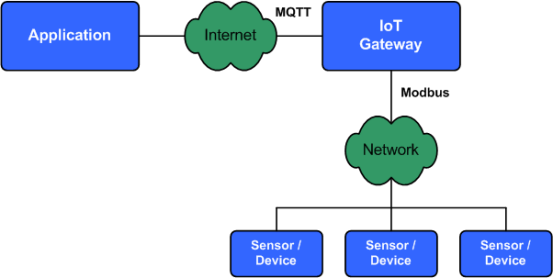
Modbus, initially developed for industrial automation, has become a popular protocol in various IoT applications. It supports multiple physical layers, such as RS-232 and TCP/IP, and offers simple and robust communication between devices. The master-slave architecture allows devices, such as sensors and actuators, to communicate with a central control system, enabling efficient monitoring and control of diverse processes.
Often, IoT systems incorporate both MQTT and Modbus devices. In such cases, MQTT acts as a communication bridge between Modbus devices and other MQTT-enabled devices or applications. By subscribing to Modbus data, converting it into MQTT format, and publishing it to MQTT topics, Modbus devices can seamlessly integrate with the larger IoT ecosystem.
The integration of MQTT and Modbus offers several advantages in the IoT context:
a) Interoperability: MQTT provides a standardized and interoperable messaging layer for Modbus devices, ensuring seamless integration with other IoT components.
b) Scalability: MQTT's pub/sub model allows for flexible and scalable communication, accommodating a growing number of Modbus devices.
c) Security: MQTT supports authentication and encryption, enhancing the security of Modbus communications in IoT systems.
The complementary nature of MQTT and Modbus enables various IoT use cases:
a) Industrial Automation: MQTT can be used to connect Modbus-enabled devices in industrial automation, enabling real-time monitoring and control of processes.
b) Energy Management: Integration of Modbus energy meters with MQTT platforms allows for centralized monitoring and analysis of energy consumption in smart buildings.
c) Remote Monitoring: MQTT's lightweight protocol can be used to collect data from remote Modbus sensors and transmit it to a central server for analysis and decision-making.
In conclusion, MQTT and Modbus are complementary protocols that, when used together, enhance the overall functionality and interoperability of IoT systems. MQTT acts as a bridge, enabling Modbus devices to seamlessly communicate with other IoT components. The integration of these protocols opens up a wide range of possibilities for industrial automation, energy management, and remote monitoring applications in the IoT landscape.
 Trolink Joint With Tuya to Make Iot Benefit Every Family
Trolink Joint With Tuya to Make Iot Benefit Every Family
 5 Key Indicators for WiFi Module Selection You Have to Know !
5 Key Indicators for WiFi Module Selection You Have to Know !
 IOT module is the brain of smart products
IOT module is the brain of smart products
 What is the signal coverage range of the WiFi module chip?
What is the signal coverage range of the WiFi module chip?